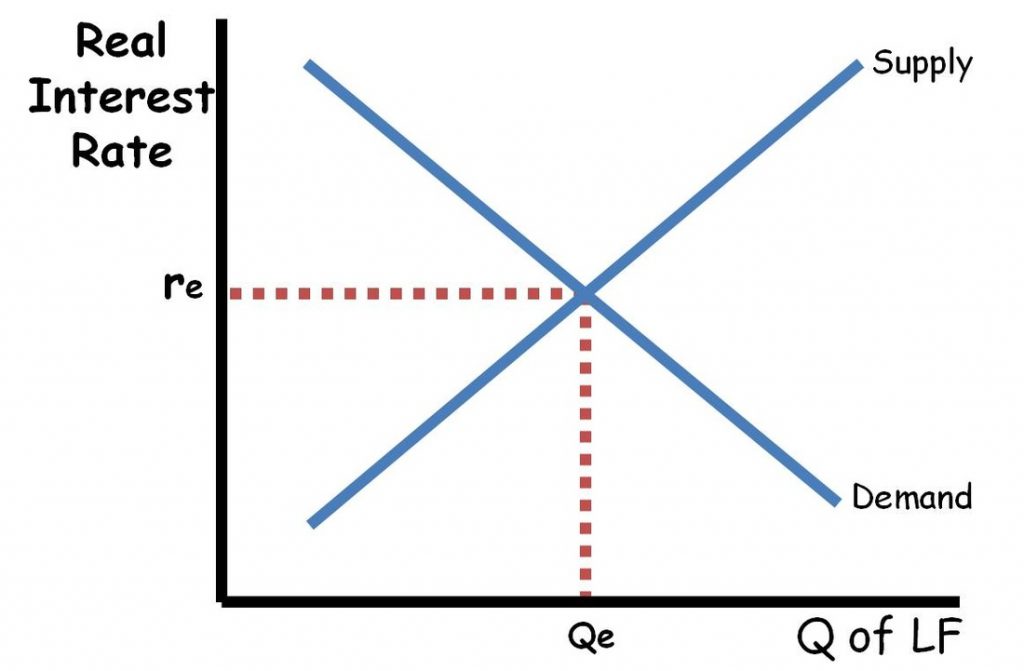
Loanable Funds Market
- The market where savers and borrowers exchange funds (QLF) at the real rate of interest (r%)
- The demand for loanable funds or borrowing comes from households, firms, government, and the foreign sector. The demand for loanable funds is in fact the supply of bonds.
- The supply of loanable funds, or savings comes from households, firms, government and the foreign sector. The supply for loanable funds is also the demand for bonds.
- Remember that demand for loanable funds = borrowing (ex. supplying bonds)
- More borrowing = More demand for loanable funds (➝)
- Less borrowing = Less demand for loanable funds (←)
- Government deficit spending = more borrowing = more demand for loanable funds
- DLF shifts to the right
- Real rate of interest (r%) goes up
- Less investment demand = less borrowing = less demand for loanable funds
- DLF shifts to the left
- Real rate of interest (r%) goes down
Changes in the Supply for Loanable Funds(SLF)
- Remember that supply of loanable funds = saving(ex. demand for bonds)
- More saving = More supply of loanable funds (➝)
- Less saving = Less supply of loanable funds (←)
 |
- Government budget surplus = more saving = more supply of loanable funds
- SLF shifts to the right
- r% goes down
- Decrease in consumers' MPS = less saving = less supply of loananble funds
- SLF shifts to the left
- r% goes up
No comments:
Post a Comment